Demystifying Botulinum Toxin: How It Works
Understanding Botulinum Toxin
Botulinum toxin, often referred to as Botox, is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium *Clostridium botulinum*. While it may sound intimidating, this substance has found a significant place in both medical and cosmetic fields. From smoothing wrinkles to treating medical conditions like migraines and muscle spasms, botulinum toxin is versatile and widely used. But how exactly does it work? In this post, we'll delve into the science behind botulinum toxin and its various applications.
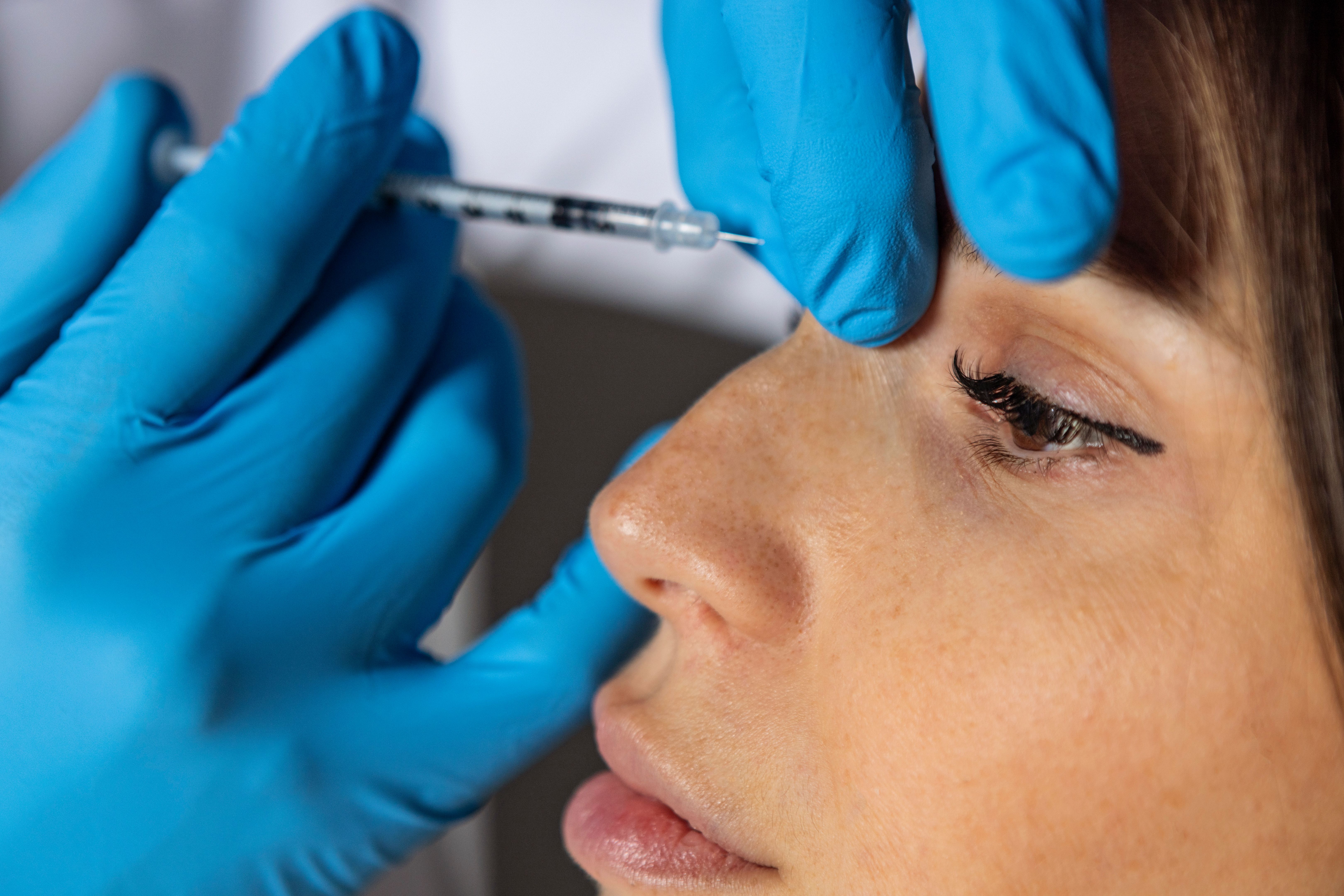
The Science Behind Botulinum Toxin
Botulinum toxin works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter responsible for muscle contraction. When injected into specific muscles, it causes temporary paralysis or relaxation of those muscles. This effect is what makes it valuable for both cosmetic and therapeutic purposes. The toxin's ability to interfere with nerve signals is what allows it to smooth out wrinkles and alleviate muscle-related conditions.
Interestingly, botulinum toxin is one of the most potent toxins known to humans. However, when used in controlled doses by trained professionals, it is safe and effective. Its potency and precision make it an invaluable tool in various medical treatments.
Cosmetic Uses of Botulinum Toxin
In the world of aesthetics, botulinum toxin is best known for its ability to reduce the appearance of facial wrinkles. It is commonly used on areas such as the forehead, between the eyebrows, and around the eyes to create a smoother, more youthful appearance. The effects are temporary, lasting anywhere from three to six months, after which further treatments may be necessary.
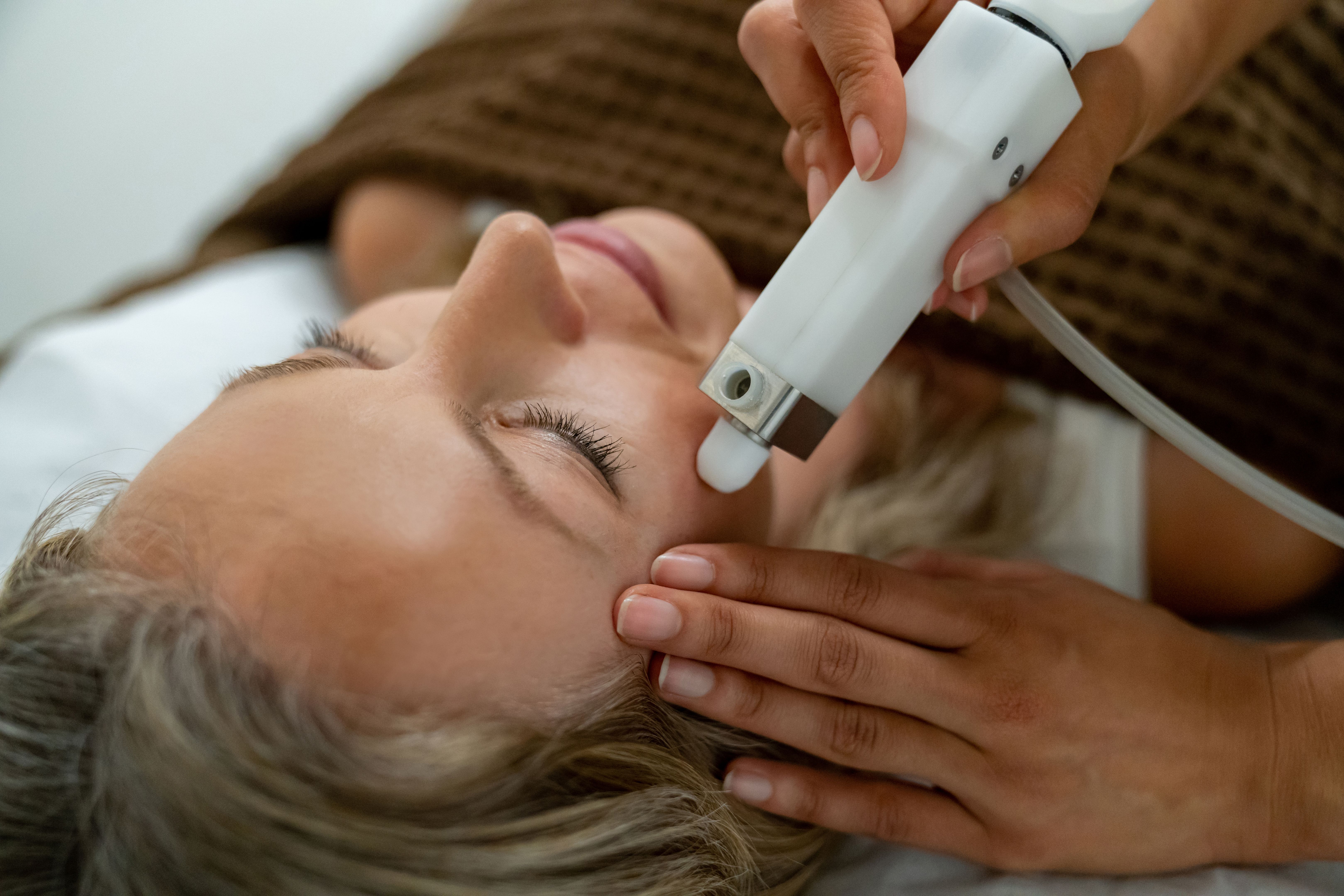
Patients often appreciate the minimally invasive nature of botulinum toxin treatments. With no significant recovery time required, individuals can resume their normal activities almost immediately. This convenience has contributed to its popularity as a cosmetic procedure.
Therapeutic Applications
Beyond its aesthetic uses, botulinum toxin plays a crucial role in managing various medical conditions. It is used to treat chronic migraines by reducing the frequency and severity of headache attacks. Additionally, it is effective in managing muscle spasticity disorders such as cerebral palsy and multiple sclerosis.
- Chronic migraines
- Spasticity disorders
- Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating)
Another noteworthy application is in the treatment of hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating. Botulinum toxin injections can significantly reduce sweating in targeted areas such as the underarms, palms, and soles of the feet.
Safety and Considerations
While botulinum toxin is generally safe, it is essential that treatments are administered by qualified medical professionals. Incorrect application can lead to complications such as unintended muscle weakness or asymmetry. Patients should disclose their medical history and any current medications to ensure safety and efficacy.

Side effects are typically mild and temporary, including bruising or swelling at the injection site. Rarely, more serious side effects can occur, so it's important to have open communication with your healthcare provider.
The Future of Botulinum Toxin
The use of botulinum toxin continues to expand as research uncovers new potential applications. Scientists are exploring its use in treating conditions like depression and chronic pain. As our understanding grows, so too does the potential for botulinum toxin to improve quality of life for those with various medical concerns.
In conclusion, botulinum toxin is a powerful tool with a wide range of applications. Whether for cosmetic enhancement or therapeutic relief, its benefits are well-documented when used responsibly and professionally.